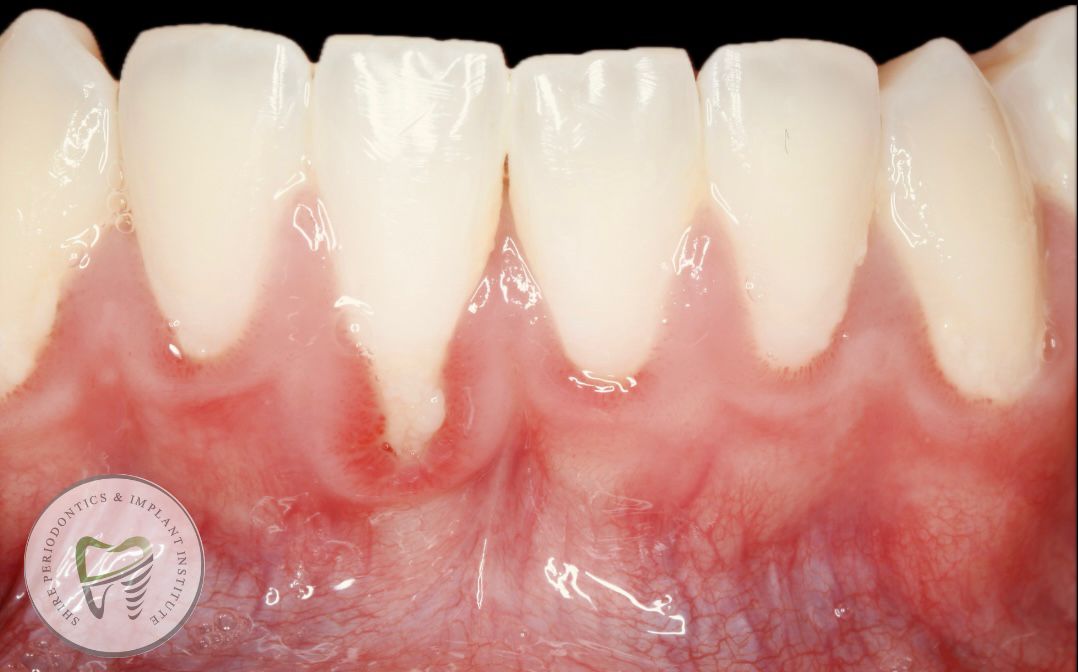
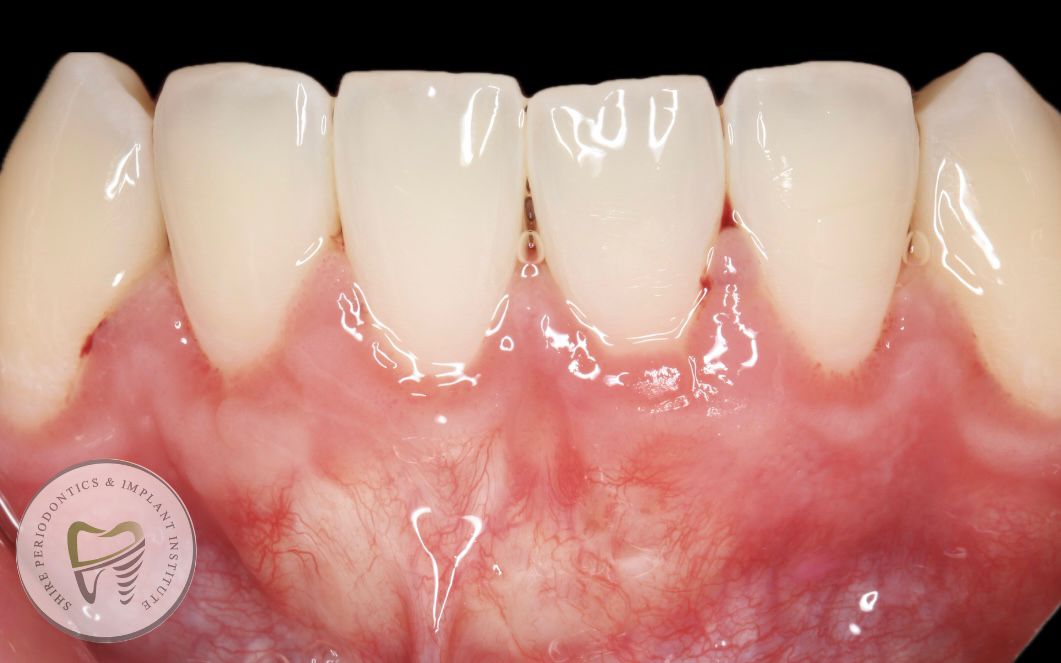
What is gum recession?
Gum recession, or gingival recession, is a condition where the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth or the tooth’s root.
What causes gum recession?
Common causes include aggressive tooth brushing, periodontal disease, genetics, tobacco use, and hormonal changes (such as those during pregnancy).
What are the symptoms of gum recession?
Symptoms include longer-looking teeth, increased tooth sensitivity, visible roots, and gaps between teeth.
Can gum recession be reversed?
Mild cases of gum recession can sometimes be managed with improved oral hygiene and professional treatments, but once the gum tissue is lost, it cannot grow back on its own.
How is gum recession diagnosed?
A dentist or periodontist diagnoses gum recession through a visual examination, measuring the depth of the gum pockets and recession, and possibly taking X-rays to assess bone loss.
What treatments are available for gum recession?
Treatments range from non-surgical options like scaling and root planing to surgical procedures such as gum grafts, which involve taking tissue from another part of the mouth and attaching it to the affected area.
How can I prevent gum recession?
Preventive measures include practising good oral hygiene, using a soft-bristled toothbrush, avoiding tobacco, and visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
Is gum recession hereditary?
Yes, genetics can play a role in gum recession. If your parents or close relatives have experienced gum recession, you may be more likely to develop it as well.
Can gum recession lead to other dental problems?
Yes, gum recession can lead to increased tooth sensitivity, root decay, and even tooth loss if left untreated.
What lifestyle changes can help improve gum health and prevent recession?
Quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, and avoiding aggressive tooth brushing can all help improve gum health and prevent recession.